Chapter 9: Gandhara and the Silk Road — FAQ
WeiYifanShare
Why is Gandhara closely linked to the Silk Road?
Because Gandhara lay at a critical junction of the southern Silk Road. Merchants, monks, and envoys traveling between India, Central Asia, Persia, and the Mediterranean all passed through it. Gandhara became a true “cultural crossroads.”
⸻
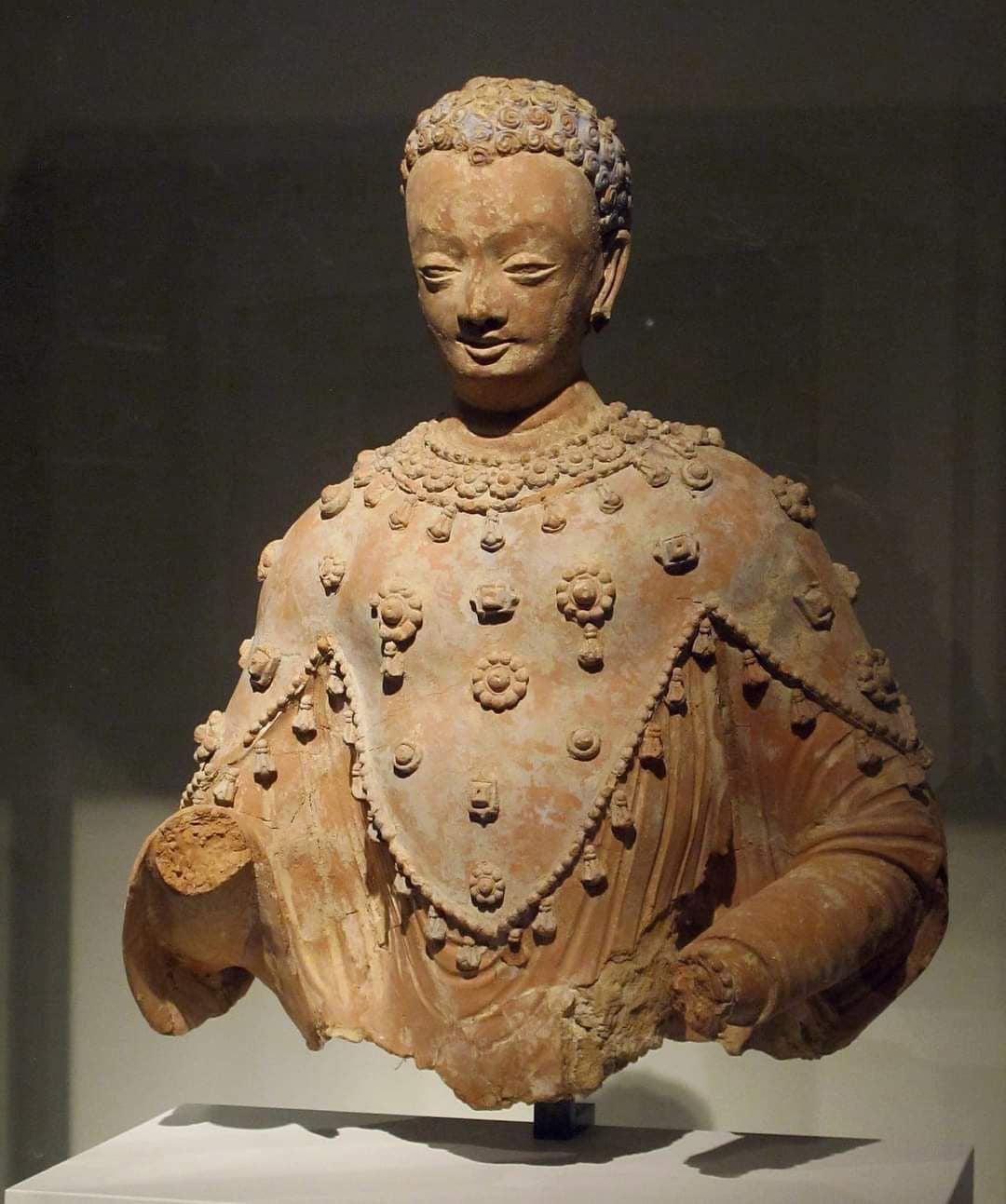
How did the Silk Road influence Gandhara art?
• Greek and Roman styles shaped the realistic features of Buddha statues.
• Persian royal motifs appeared in stupa decorations.
• Indian Buddhist narratives formed the thematic foundation.
The Buddha in Gandhara wears a “Greek-style robe” but tells an Indian story — a living product of Silk Road exchanges.
⸻
How did Buddhism spread through Gandhara?
• Monks traveled from Gandhara to Central Asia, Turfan, Dunhuang, and eventually Chang’an.
• Texts were translated into Kharosthi, Pali, and Sanskrit, then later into Chinese.
• Gandhara’s artistic style influenced early Buddhist sculpture in China.
⸻
What has modern archaeology revealed?
Excavations in Xinjiang, Afghanistan, and Pakistan uncovered fragments of Gandharan statues and manuscripts, offering concrete proof of Silk Road exchanges.
⸻
Gandhara was the Buddhist hub of the Silk Road. It proves that the Silk Road was not only about goods, but also about ideas and aesthetics.