Chapter 1: Gandhara Art Studies
WeiYifanShare
Gandhara art emerged between the 1st and 5th centuries CE in the ancient Gandhara region, now at the border of Pakistan and Afghanistan. Situated at the crossroads of Indian civilization and Hellenistic culture, Gandhara Buddhist sculptures combine Indian religious symbolism with Hellenistic sculptural techniques. Buddha statues, reliefs, stucco, and schist fragments not only showcase exquisite craftsmanship but also carry historical information on the spread of Buddhism. This blog systematically organizes and analyzes these artifacts, providing a scholarly resource for researchers, collectors, and art enthusiasts.
Gandhara Buddha Sculpture Studies
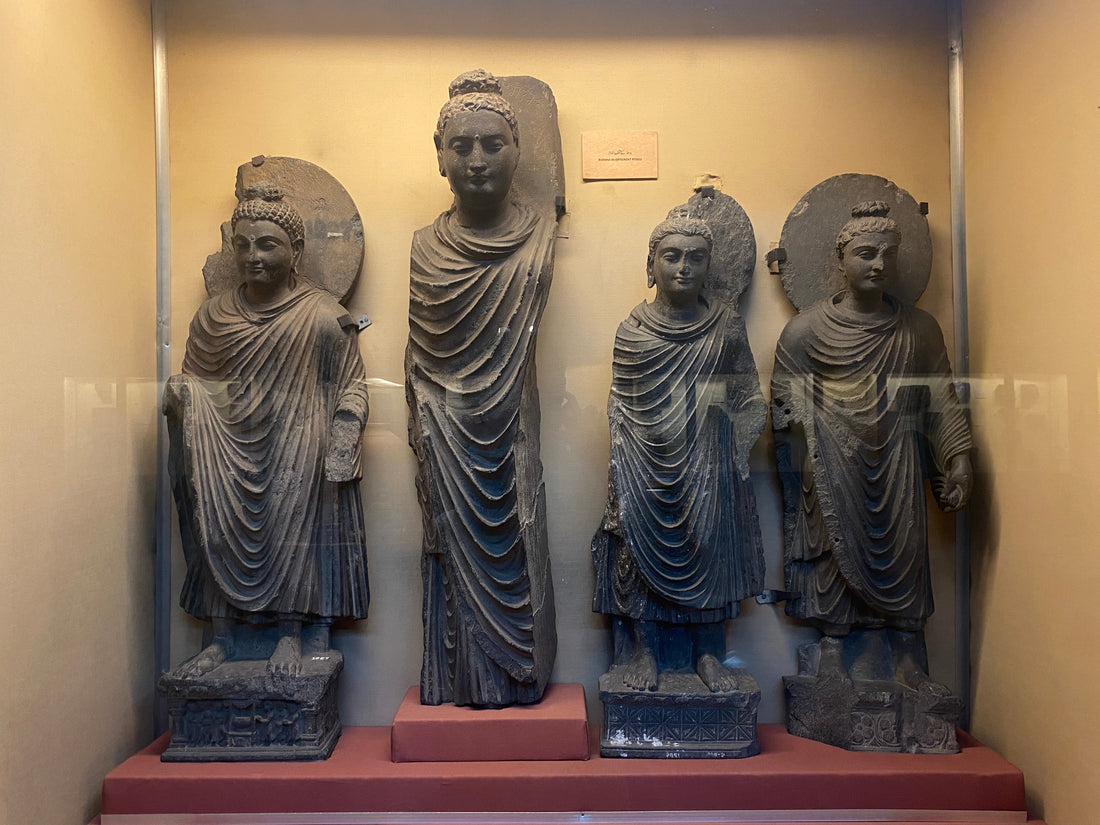
Buddha statues are central to Gandhara art. Complete heads, torsos, hands, and fragments demonstrate a fusion of Indian Buddhist iconography and Hellenistic sculptural style. Buddha heads typically feature finely carved brows and lowered eyes, conveying serenity and compassion; torsos display defined drapery and fluid lines, reflecting Hellenistic body proportions and sculptural skill. Studying fragments allows scholars to reconstruct original forms, understand carving processes, and analyze stylistic changes over time.
Gandhara Relief Studies
Reliefs are crucial for understanding Gandhara Buddhist culture. Subjects include Jataka tales, donor figures, and deities. Reliefs are primarily in schist and stucco, employing low or high relief techniques. Fragment analysis allows study of carving tools, methods, stylistic evolution, and donor systems. Damaged surfaces and traces of color provide information on historical context and craftsmanship.
Art Style & Historical Context
Gandhara art merges Indian Buddhist iconography with Hellenistic sculptural style, showing Greek-influenced body proportions, drapery dynamics, and facial expressions. Donor figures reflect social structures and religious systems, providing cultural context for the spread of Buddhism.
Collecting & Archaeological References
This blog provides scholarly resources, collection appreciation, and archaeological findings. Analysis of excavated fragments, restoration records, and literature helps understand the historical value and cultural significance of Gandhara art.